The Oceans Portal
A portal dedicated to oceans, seas, oceanography and related topics
– Hover over image and scroll to middle for controls to see more selected panorama images –
Introduction
| Earth's ocean |
|---|
|
Main five oceans division: Further subdivision: Marginal seas |

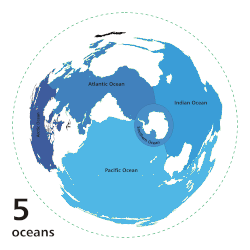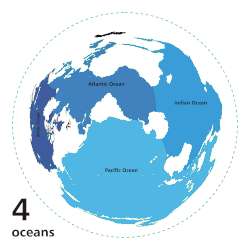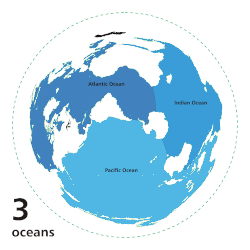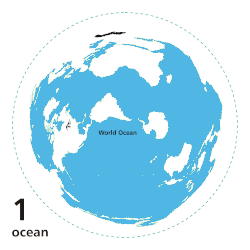
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as oceans (in descending order by area: the Pacific Ocean, the Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, the Antarctic/Southern Ocean, and the Arctic Ocean), and are themselves mostly divided into seas, gulfs and subsequent bodies of water. The ocean contains 97% of Earth's water and is the primary component of Earth's hydrosphere, acting as a huge reservoir of heat for Earth's energy budget, as well as for its carbon cycle and water cycle, forming the basis for climate and weather patterns worldwide. The ocean is essential to life on Earth, harbouring most of Earth's animals and protist life, originating photosynthesis and therefore Earth's atmospheric oxygen, still supplying half of it. (Full article...)

A sea is a large body of salt water. There are particular seas and the sea. The sea commonly refers to the ocean, the interconnected body of seawaters that spans most of Earth. Particular seas are either marginal seas, second-order sections of the oceanic sea (e.g. the Mediterranean Sea), or certain large, nearly landlocked bodies of water. (Full article...)
Oceanography (from Ancient Greek ὠκεανός (ōkeanós) 'ocean' and γραφή (graphḗ) 'writing'), also known as oceanology, sea science, ocean science, and marine science, is the scientific study of the ocean, including its physics, chemistry, biology, and geology. (Full article...)
Selected article -

Ocean acoustic tomography is a technique used to measure temperatures and currents over large regions of the ocean. On ocean basin scales, this technique is also known as acoustic thermometry. The technique relies on precisely measuring the time it takes sound signals to travel between two instruments, one an acoustic source and one a receiver, separated by ranges of 100–5,000 kilometres (54–2,700 nmi). If the locations of the instruments are known precisely, the measurement of time-of-flight can be used to infer the speed of sound, averaged over the acoustic path. Changes in the speed of sound are primarily caused by changes in the temperature of the ocean, hence the measurement of the travel times is equivalent to a measurement of temperature. A 1 °C (1.8 °F) change in temperature corresponds to about 4 metres per second (13 ft/s) change in sound speed. An oceanographic experiment employing tomography typically uses several source-receiver pairs in a moored array that measures an area of ocean. (Full article...)
Interesting facts -
- The deep-sea coral species Gersemia juliepackardae was named for Julie Packard (pictured), executive director of Monterey Bay Aquarium, for her work as an ocean conservationist.
- Chinese politician Liu Cigui worked as a rusticated youth and studied oceanography.
- Female seaweed blennies deposit their eggs in a shared nest where the male fish guards them until they hatch.
Selected list articles and Marine habitat topics
| Marine habitats |
|---|
| Coastal habitats |
| Ocean surface |
| Open ocean |
| Sea floor |
- List of oceans
- List of ancient oceans
- List of seas
- List of circumnavigations
- List of cruise lines
- List of largest lakes and seas in the Solar System
- List of marine biologists
- List of marine ecoregions
- List of maritime explorers
- List of naval battles
- List of ocean liners
- List of oceanographic institutions and programs
- List of oldest surviving ships
- List of rogue waves
- List of seafood dishes
- List of submarine topographical features
Tasks
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
General images -
Related portals
In the news
- 3 February 2026 – Middle Eastern crisis
- Several Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps Navy gunboats attempt to stop and seize a U.S. tanker in the Strait of Hormuz. The tanker ignored the demands to stop and continued on its journey towards the Arabian Sea under escort of a United States Navy warship. (CBS News)
- 25 January 2026 –
- A merchant ship rescues one migrant in the Mediterranean Sea after a boat departing from Tunisia sinks, while authorities report that about 50 others are missing and presumed dead and transfer the survivor to Malta for medical treatment. (Reuters)
- 25 January 2026 – Embargo of Russian oil during the Russo-Ukrainian war, France–Russia relations
- French authorities place the Indian captain of an oil tanker intercepted by the French Navy in the Mediterranean Sea under questioning on suspicion of breaching sanctions on Russian oil shipments, while prosecutors open a preliminary inquiry after the vessel arrives at anchorage near Marseille and its crew remains aboard. (AP)
- 15 January 2026 – Operation Southern Spear
- The United States Coast Guard boards and seizes a Guyanese-flagged tanker in the Caribbean Sea that had been sanctioned by the U.S. government. (The Guardian)
- 7 January 2026 – Operation Southern Spear
- The United States boards and seizes the sanctioned Russian-flagged tanker Marinera (Bella 1) in the North Atlantic Ocean after it breached the U.S. naval blockade around Venezuela. (Reuters) (Sky News)
WikiProjects
Topics
Categories
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Admiralty law
| Admiralty and maritime law |
|---|
| History |
| Features |
| Contract of carriage / charterparty |
| Parties |
| Judiciaries |
| International organizations |
| International conventions |
|
| International Codes |
Need assistance?

Do you have a question about oceans, seas or oceanography that you can't find the answer to? Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk.
External media

- World Ocean Database and World Ocean Atlas Series – from the U.S. National Centers for Environmental Information, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Includes the World Ocean Atlas.
- European Atlas of the Seas – the European Atlas of the Seas, from the European Commission
- NOAA Research – NOAA research news, Oceanic and Atmospheric Research (OAR)
- Ocean Research – from The World Ocean Observatory
- Ocean Biodiversity Information System – "a global open-access data and information clearing-house on marine biodiversity for science, conservation and sustainable development"










































































![Image 73"Terres Australes" [sic] label without any charted landmass (from Southern Ocean)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8e/Geography_world_map.jpeg/120px-Geography_world_map.jpeg)